Principles of NMR metabolomics
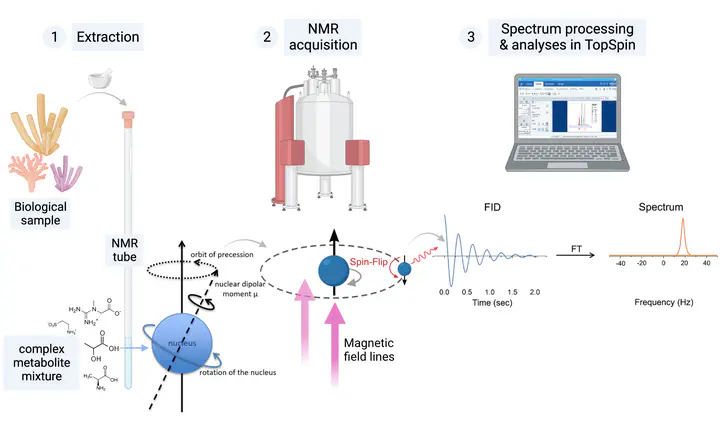
Principles of NMR metabolomics
- Biological samples are extracted yielding a complex metabolite mixture, which are transferred into an NMR tube
- During NMR acquisition a strong homogenous magnetic field aligns the nuclear spins of the atoms present in the sample by using the same resonance frequency of the nuclei (Larmor Frequency). The nuclear spins are magnetized and resonate. After the magnetic pulse, spins ‘flip back’ to their natural state (thermal equilibrium) and their relaxation times yield a measurable signal, the free induction decay (FID).
- The FID is translated via Fourier-Transformation (FT) into frequencies (Hz) and yield the final metabolomics spectrum, which can be processed and analysed for metabolite identification and abundance analyses.
Literature
Atta-Ur-Rahman, T.I., 2012. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: Basic Principles. Springer Science & Business Media.
Carreras, H., 2021. NMR Spectroscopy Principles, Interpreting an NMR Spectrum and Common Problems. Technology Networks.
Diehl, P., Khetrapal, C.L., Jones, R.G., 2013. NMR Basic Principles and Progress. Grundlagen und Fortschritte. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Larive, C.K., Gregory A. Barding, J., Dinges, M.M., 2014. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics and Metabolic Profiling. ACS Publications. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504075g